As we age, our skin tells our life story. Unexpected aging skin growths can feel like unwanted visitors. They show up quickly and can change how we see ourselves.
Aging skin growths are more than just looks. They show how our skin reacts to time, our surroundings, and our genes. Knowing about these growths helps us deal with aging better.
About 85% of people over 50 see changes in their skin. This is because melanocytes decrease, fat moves, and the environment affects us. It’s important to understand these changes.
Key Takeaways
- Skin changes are natural signs of aging process
- 85% of people over 50 experience visible skin transformations
- Aging skin growths can occur in various body areas
- Sun exposure significantly influences skin changes
- Regular skin monitoring is essential for early detection
The Science Behind Aging Skin Changes
Our skin is a complex organ that changes a lot as we age. Knowing how skin aging works helps us understand why we get aging skin growths and age spots.
The human skin has three main layers. Each layer is important for protecting us and how we look:
- Epidermis: The outermost protective layer
- Dermis: The middle layer with connective tissues
- Subcutaneous layer: The deepest layer with fat and tissue
Structure and Function of Skin Layers
As we get older, these layers change a lot. Epidermal thinning starts early, making our skin less protective. The dermis loses collagen, making it less strong. This helps create aging skin growths.
Role of Environmental Factors
“Skin aging is a complex interplay between internal and external influences” – Dermatological Research Institute
Things outside of us speed up skin aging a lot. UV radiation is the biggest problem, causing cell damage that leads to age spots. Pollution, lifestyle, and sun exposure all affect how our skin ages.
Impact of Genetics and Pigmentation
Our genes play a big part in how our skin ages. Young and old skin have different genes that affect how cells work and how we fight off diseases. Some people are more likely to get certain aging skin growths because of their genes.
- Melanocyte reduction affects skin pigmentation
- Genetic factors influence collagen production
- Individual skin repair mechanisms vary
Knowing these scientific facts helps us make better choices for our skin health and how to prevent problems.
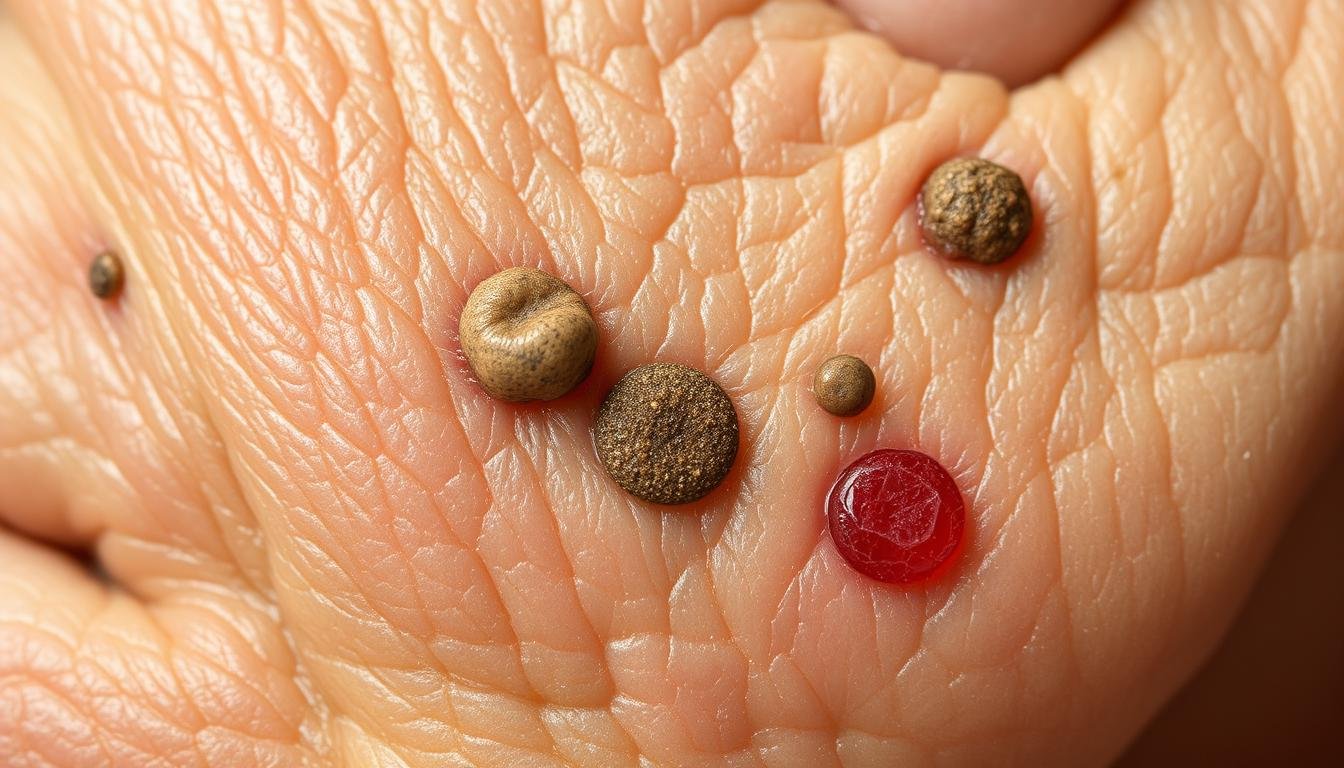
Common Types of Aging Skin Growths
As we age, our skin changes a lot. It develops growths that can look mysterious and worry us. Knowing about these growths helps us keep our skin healthy and spot problems early.
Getting older means our skin goes through many changes. People often see different growths as they age. These can be anything from harmless moles to more serious skin issues.
Identification and Characteristics
Our skin can grow several types of growths, including:
- Skin tags: Small, soft growths in skin folds
- Seborrheic keratoses: Waxy, brown or tan spots
- Actinic keratoses: Rough, scaly patches from sun damage
- Moles: Pigmented spots that vary in size and color
When to Seek Medical Attention
“Not all skin growths are dangerous, but some require professional evaluation.”
See a dermatologist if you notice:
- Changes in size or color of moles
- Irregular borders on skin lesions
- Growths that bleed or hurt
- New growths that look unusual
Risk Factors and Prevention
Many things can make skin growths more likely:
- Sun exposure: Too much UV radiation raises risk
- Genetic predisposition
- Age and hormonal changes
- Skin type and pigmentation
Protect your skin with sunscreen, regular check-ups, and good health. This can help reduce unwanted skin changes.
Seborrheic Keratoses: The Most Common Age-Related Growths
Seborrheic keratoses are very common skin growths that show up more as we get older. About 80% of adults over 50 get these growths. They are a common sign of aging skin.
These skin growths can look different:
- Colors ranging from light tan to brown or black
- Sizes from tiny spots to over 1 inch in diameter
- Waxy or scaly texture
- Often described as looking “pasted on” the skin
Seborrheic keratoses often pop up on sun-exposed areas, like:
- Face
- Neck
- Chest
- Shoulders
- Back
Even though they’re harmless, they can sometimes bother people. People with a family history are more likely to get seborrheic keratoses. This shows they have a strong genetic link.
A special type called dermatosis papulosa nigra is common in darker skin tones. It usually shows up around the eyes.
There are ways to remove these growths if you want to. You can try cryotherapy, electrosurgery, or laser therapy. These methods can help if you’re worried about how they look or if they’re bothering you.
Understanding Actinic Keratoses and Sun Damage
Actinic keratoses are a serious skin condition caused by too much sun. They appear as rough, scaly patches. These patches can be a sign of skin cancer if not treated.
Ultraviolet radiation changes our skin, making actinic keratoses a big worry. These growths often show up in sun-prone areas like the face, ears, neck, and hands.
Early Detection Signs
Spotting actinic keratoses early is key to avoiding skin cancer. Look out for these signs:
- Rough, dry, or scaly skin patches
- Patches smaller than 1 inch in diameter
- Reddish, pinkish, or tan-colored lesions
- Persistent skin texture changes
*”Early detection can significantly reduce the risk of progression to skin cancer”* – Dermatology Research Institute
Treatment Options Available
Our dermatologists suggest several treatments for actinic keratoses:
| Treatment Method | Duration | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Cryotherapy | 5-10 days (face) | High |
| Topical 5-Fluorouracil | 2-8 weeks | Moderate to High |
| Diclofenac Gel | 3 months | Moderate |
Prevention is the best approach. Use SPF 30 sunscreen, avoid midday sun, and get regular skin checks. This helps catch actinic keratoses early.
Note: Up to 25% of people aged 60 and over in certain regions may develop actinic keratoses, underscoring the importance of proactive skin health management.
Age Spots and Lentigines: Causes and Treatment
Age spots, also known as lentigines, are common skin changes that appear with age. They are tan or brown spots that show up on sun-exposed areas like the face and hands.
About 90% of adults over 50 get age spots. UV radiation is a big reason why, causing about 80% of skin aging signs.
“Understanding age spots is key to managing their appearance and preventing further skin damage.”
Several factors contribute to age spots:
- Cumulative sun exposure
- Genetic predisposition
- Hormonal changes
- Certain medications
Preventing lentigines is important. The American Academy of Dermatology suggests:
- Using broad-spectrum sunscreen (SPF 30+)
- Avoiding peak UV hours (10 a.m. to 4 p.m.)
- Wearing protective clothing
- Seeking shade when possible
There are treatments for age spots:
| Treatment Method | Effectiveness Rate | Recovery Time |
|---|---|---|
| Laser Therapy | 70-80% | Less than 10 days |
| Chemical Peels | Up to 50% | 7-14 days |
| Cryotherapy | 80% | 1-2 weeks |
Even though age spots are usually harmless, it’s wise to check them with a dermatologist. This can help avoid skin cancer. Keeping your skin protected from the sun can also help prevent new spots.
Skin Tags and Their Management
Skin tags are common, harmless growths that many people get as they age. They are small, soft, and can appear almost anywhere on the body. This can cause mild cosmetic concerns for many.
Our bodies develop skin tags through different ways. Certain factors make them more likely to form. Knowing these patterns can help manage and address these common skin growths.
Formation Patterns of Skin Tags
Skin tags usually appear in areas with a lot of friction or skin-to-skin contact. Key areas include:
- Neck regions
- Armpits
- Groin area
- Beneath breasts
- Eyelid folds
Some risk factors increase the chance of getting skin tags:
- Obesity and excess body weight
- Hormonal changes
- Genetic predisposition
- Diabetes
- Pregnancy
Removal Procedures for Skin Tags
While skin tags are harmless, some people want them removed for cosmetic or comfort reasons. Professional dermatologists offer several removal methods:
| Removal Method | Procedure Details | Recovery Time |
|---|---|---|
| Cryosurgery | Freezing skin tag | 1-3 weeks |
| Electrodesiccation | Burning skin tag | 1-3 weeks |
| Surgical Snipping | Cutting with surgical scissors | Immediate |
Important: The FDA warns against at-home removal methods due to risks. Always consult a healthcare professional for safe skin tag management.
“Nearly 50-60% of adults will develop at least one skin tag in their lifetime, with prevalence increasing after age 40.” – Dermatological Research
Understanding skin tags helps make informed decisions about skin health. Regular skin checks and professional consultations ensure proper management of these common growths.
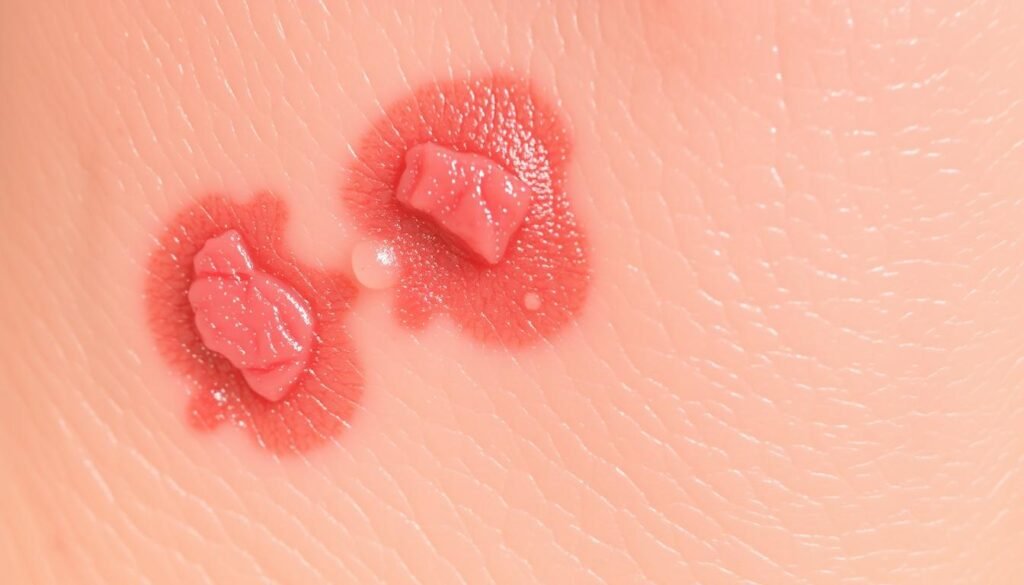
Cherry Angiomas: Red Spots in Aging Skin
Cherry angiomas are small, bright red spots that grow more common with age. They usually show up on the chest, back, and belly. About 75% of people over 75 get these red spots.
Cherry angiomas have a few key traits:
- They are 1 to 5 millimeters in size.
- They are bright red or cherry-red.
- They look smooth and dome-shaped.
- They are painless and usually harmless.
Even though cherry angiomas are mostly harmless, they can bleed if hurt. Around 5% of teens also get them, showing they’re not just for older people.
Medical experts say to watch cherry angiomas for any big changes in size, color, or shape.
Several things can make cherry angiomas appear, including:
- Genetics
- Hormonal shifts
- Exposure to certain things in the environment
- Underlying health issues
If you’re worried about cherry angiomas, talking to a doctor is a good idea. They can suggest treatments like pulsed dye laser (PDL) that work well and don’t hurt much.
The Role of Sun Exposure in Skin Changes
Sun exposure greatly affects our skin’s health and looks, more so as we get older. Knowing how ultraviolet radiation and aging skin growths are linked helps us protect our skin better.
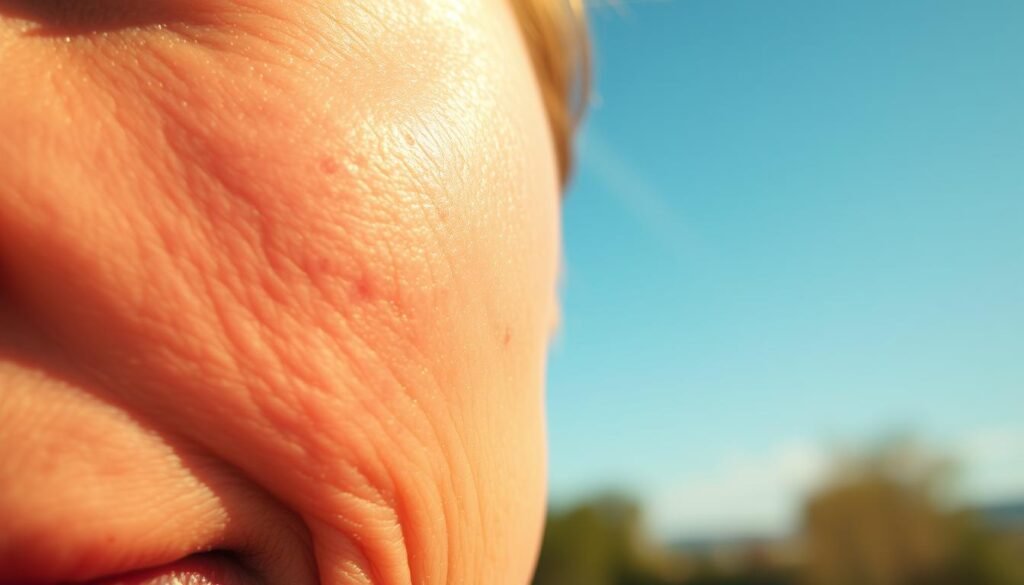

Ultraviolet (UV) radiation is key in skin aging and growths. It causes many changes that speed up the skin’s aging.
UV Damage Prevention Strategies
To shield our skin from UV rays, we need a few key steps. Here are some important ones:
- Use broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher
- Wear protective clothing that covers exposed skin
- Seek shade during peak sunlight hours (10 AM – 4 PM)
- Wear wide-brimmed hats and UV-blocking sunglasses
Protective Measures Against Sun Damage
Using strong sun protection can greatly lower the risk of aging skin growths. Studies show that regular protection can lessen damage.
| UV Ray Type | Skin Impact | Protection Level |
|---|---|---|
| UVA | Causes premature aging | Broad-spectrum sunscreen |
| UVB | Primary cause of sunburn | High SPF protection |
*”Prevention is always better than cure when it comes to protecting your skin from sun damage.”*
As we age, our skin’s repair skills get weaker. So, protecting our skin from the sun is more important than ever. By understanding UV radiation’s effects and using strong protection, we can keep our skin healthy and strong for life.
Natural Aging Process and Skin Elasticity
As we age, our skin changes a lot. The natural aging process affects how elastic and resilient our skin is. The outer skin layer (epidermis) gets thinner, making it less protective.
Some key changes in aging skin include:
- Less collagen production
- Less elastin formation
- Cells regenerate slower
- Less moisture retention
The breakdown of connective tissue is called elastosis. It affects skin strength and flexibility. Our skin can’t bounce back as well, leading to more visible signs of aging.
“Aging is not lost youth but a new stage of opportunity and strength.” – Betty Friedan
Knowing about these changes helps us create better skincare plans. We need to protect our skin, keep it hydrated, and support cell health to fight aging skin growths.
| Skin Aging Factors | Impact Percentage |
|---|---|
| Epidermal Thickness Reduction | 6.4% per decade |
| Sebum Production Decrease | 60% reduction |
| Melanocyte Activity Decline | 8-20% per decade |
By starting skincare early and understanding our body’s aging, we can handle skin aging better.
Dermatosis Papulosa Nigra in Different Skin Types
Dermatosis papulosa nigra (DPN) is a skin condition mostly seen in darker skin tones. It’s a fascinating topic that affects millions globally.
DPN is a skin growth pattern that gets more noticeable with age. Studies show that up to one-third of African American adults have it. This makes it very common in darker-skinned populations.
Ethnic Variations and Prevalence
Looking into the ethnic sides of dermatosis papulosa nigra gives us important info:
- It’s most common in people with darker skin types III to VI.
- It affects 10% to 75% of those with darker skin.
- Women are twice as likely to get DPN as men.
- It usually starts in the teens.
Treatment Approaches
There are many ways to treat DPN, each with its own benefits:
- Cryotherapy
- Electrocautery
- Laser treatments (Nd:YAG or CO2 laser)
- Curettage
Even though DPN is hard on the looks, it’s not harmful. Treatments can make the spots less noticeable. But, it’s best to see a dermatologist who knows how to treat different skin types to avoid scars.
Knowing your skin’s special needs is key to managing it well.
Prevention Strategies for Healthy Aging Skin
Protecting your skin from aging growths needs a mix of strategies. Our skin changes with age, losing collagen at a rate of 1% each year. Knowing these changes helps us find the best ways to prevent them.
Here are some key ways to prevent aging skin growths:
- Daily sun protection with broad-spectrum SPF 30 sunscreen
- Wearing protective clothing and wide-brimmed hats
- Seeking shade during peak UV hours
- Maintaining a nutrient-rich diet
- Staying well-hydrated
Ultraviolet light is the main cause of skin aging. So, protecting your skin from the sun is very important. The American Academy of Dermatology says to reapply sunscreen every two to three hours, more often if you’re outside.
“Prevention is always better than cure when it comes to skin health.”
What you eat is also key to keeping your skin healthy. Eating foods high in antioxidants and taking vitamins C and E can fight off aging. Also, using a gentle skincare routine helps keep your skin’s barrier strong.
How you live your life also matters. Quitting smoking, managing stress, getting enough sleep, and eating well can all help your skin. These habits can lower your risk of getting aging skin growths.
Medical Treatments and Removal Options
When skin lesions become bothersome or raise medical concerns, patients have many treatment options. Our dermatology experts offer both surgical and non-invasive solutions. These are tailored to individual skin conditions and patient preferences.
Surgical procedures provide direct approaches for removing problematic skin lesions. Techniques like excision allow complete removal of growths. This is useful for suspicious or potentially cancerous skin changes.
Cryosurgery uses extreme cold to freeze and eliminate unwanted skin growths. Electrodesiccation uses electrical current to destroy targeted tissue.
Non-surgical treatments offer less invasive alternatives for managing skin lesions. Laser skin resurfacing can effectively minimize surface irregularities and treat fine scars. Microdermabrasion targets uneven outer skin layers, helping improve skin texture and appearance.
Intense pulsed light (IPL) therapy provides another option for addressing skin discoloration and age-related changes without surgical intervention.
Our approach considers individual skin type, growth characteristics, and patient health history when recommending treatment. Individuals between 40 to 55 years old most frequently seek these interventions. Over 4 million wrinkle-relaxing treatment injections were administered in 2020, showing the growing popularity of such solutions.
Surgical Procedures
Surgical removal remains a precise method for addressing persistent or concerning skin lesions. Techniques vary based on the specific growth. Some procedures focus on complete excision, while others target minimal tissue disruption.
Our specialists carefully evaluate each case to recommend the most appropriate surgical approach.
Non-invasive Solutions
Non-surgical treatments offer gentler alternatives for managing skin lesions. Options like chemical peels, topical medications, and laser therapies can effectively address surface irregularities. These approaches are beneficial for patients seeking minimal intervention and reduced healing periods.