Non-Melanoma Skin Cancers
Non-melanoma skin cancers are the most common types of skin cancer. There are two main types of non-melanoma skin cancer: basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma.
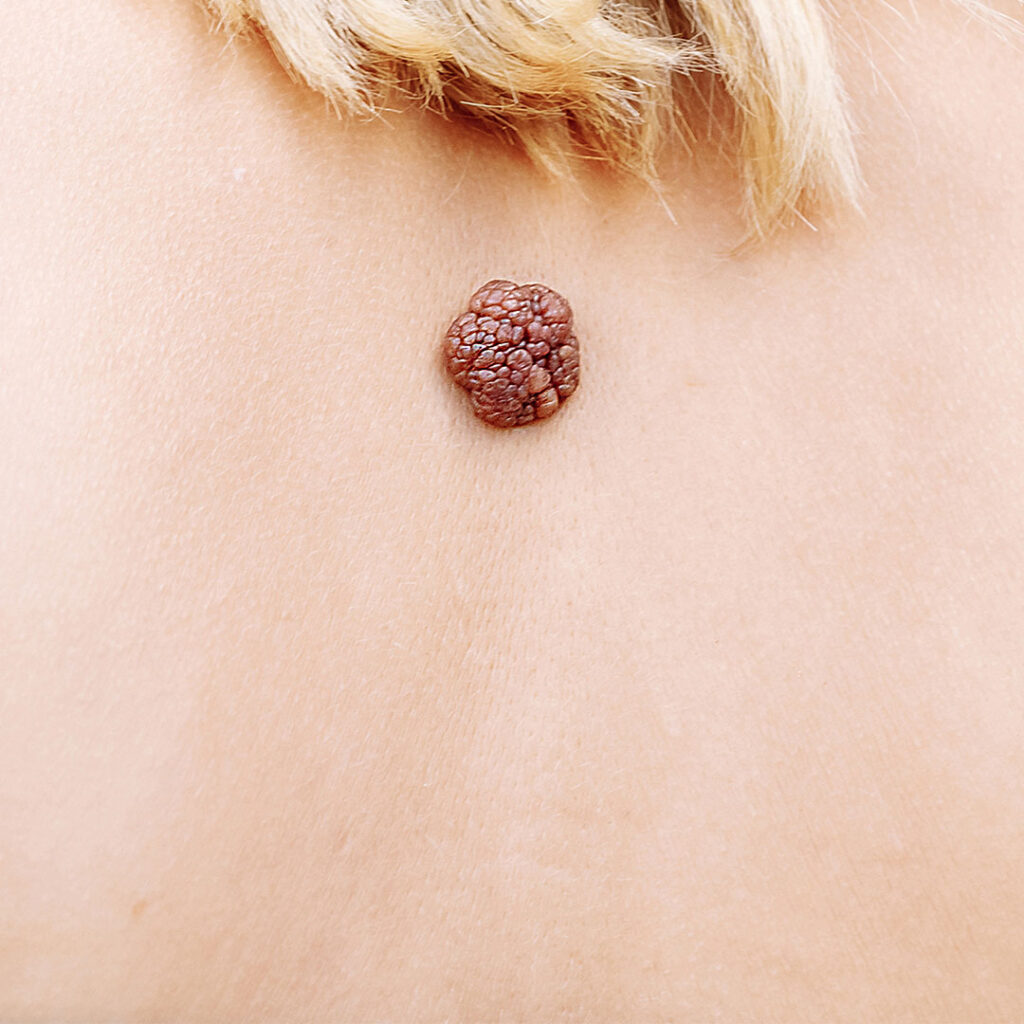
Basal cell carcinoma: Basal cell carcinoma is the most common type of skin cancer and is caused by damage to the DNA of skin cells, typically from exposure to UV radiation from the sun. Basal cell carcinomas often appear as small, fleshy bumps or growths on the skin that may bleed or crust over and do not heal.
Squamous cell carcinoma: Squamous cell carcinoma is a less common type of skin cancer but can be more aggressive than basal cell carcinoma. It is also caused by damage to the DNA of skin cells, usually from exposure to UV radiation from the sun. Squamous cell carcinomas often appear as rough, scaly patches or raised growths on the skin that may be red, pink, or flesh-colored.


Basal Cell Carcinomas (BCC)
Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is the most common type of skin cancer, affecting about one million people in the United States each year. BCCs develop in the basal cells, which are located at the base of the outermost layer of the skin. They typically grow slowly and rarely spread to other parts of the body. However, if left untreated, BCCs can invade nearby tissues and cause significant damage. Treatment options for BCCs include surgical excision, radiation therapy, and topical medications.
Causes :
The primary cause of basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is long-term exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or artificial sources such as tanning beds. Other factors that may increase the risk of developing BCC include fair skin, light hair, blue or green eyes, a history of sunburns, and a weakened immune system. Some genetic disorders, such as Gorlin syndrome, also increase the risk of BCC. It’s important to protect your skin from UV radiation by wearing protective clothing, using sunscreens, and seeking shade when the sun is strongest.
Squamous Cell Carcinomas (SCC)
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) is a type of skin cancer that affects the squamous cells, which are located in the outermost layer of the skin. It is less common than basal cell carcinoma (BCC), but it is more likely to spread (metastasize) to other parts of the body. SCC typically appears as a rough, scaly patch or open sore that may bleed or crust over. Like BCC, SCC is primarily caused by long-term exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or artificial sources such as tanning beds. Other risk factors include fair skin, a history of sunburns, a weakened immune system, and exposure to certain chemicals and industrial materials. Treatment options for SCC include surgical excision, radiation therapy, and topical medications. It’s important to protect your skin from UV radiation and to have any suspicious skin changes evaluated by a healthcare provider.
Causes :
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) is primarily caused by long-term exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or artificial sources such as tanning beds. Other factors that may increase the risk of SCC include fair skin, a history of sunburns, a weakened immune system, and exposure to certain chemicals and industrial materials. Additionally, individuals with certain precancerous skin conditions, such as actinic keratosis, are at higher risk of developing SCC. The risk of SCC can be reduced by protecting your skin from UV radiation, avoiding exposure to harmful chemicals, and having any suspicious skin changes evaluated by a healthcare provider.
Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer Diagnosis
The diagnosis of non-melanoma skin cancer, such as basal cell carcinoma (BCC) or squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), typically begins with a visual examination of the affected area by a healthcare provider. If the provider suspects skin cancer, a biopsy may be performed to remove a small sample of tissue for examination under a microscope. This is the only way to definitively diagnose skin cancer. In some cases, other diagnostic tests, such as a CT scan or MRI, may be used to determine if the cancer has spread to other parts of the body. Early detection and treatment of skin cancer is important for achieving the best possible outcome.



