Pre-Cancer Concerns
Precancerous skin conditions, also known as precancerous lesions, are changes in the skin that may develop into skin cancer if left untreated. Examples of precancerous skin conditions include actinic keratosis and dysplastic nevi.
Actinic keratosis is a scaly or crusty growth that develops on sun-exposed areas of the skin, such as the face, ears, neck, and hands. It is caused by long-term exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or artificial sources such as tanning beds.
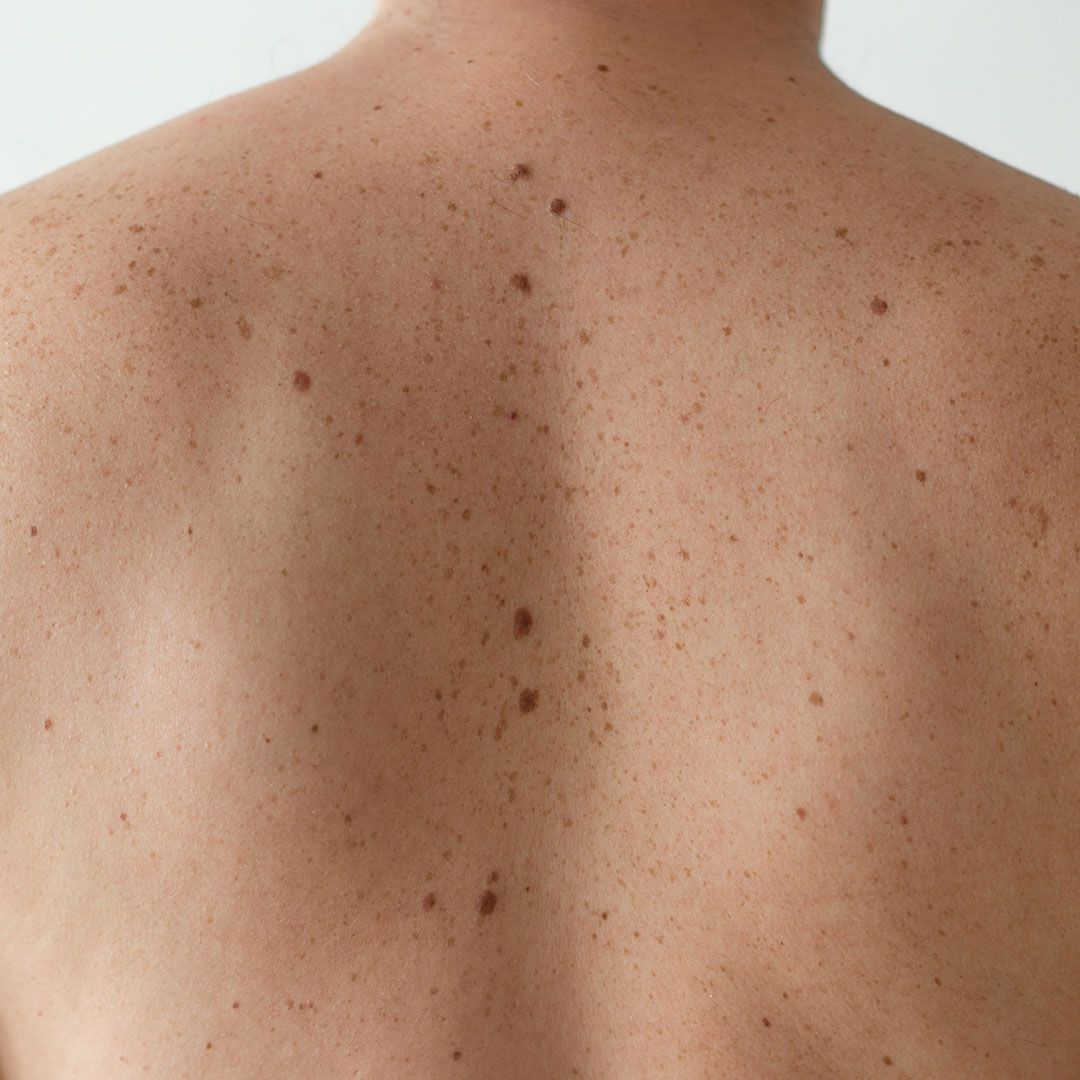
Dysplastic nevi are moles that are larger than normal, have irregular borders, and multiple colors. They have a higher risk of turning into melanoma, a type of skin cancer that can be life-threatening if left untreated.
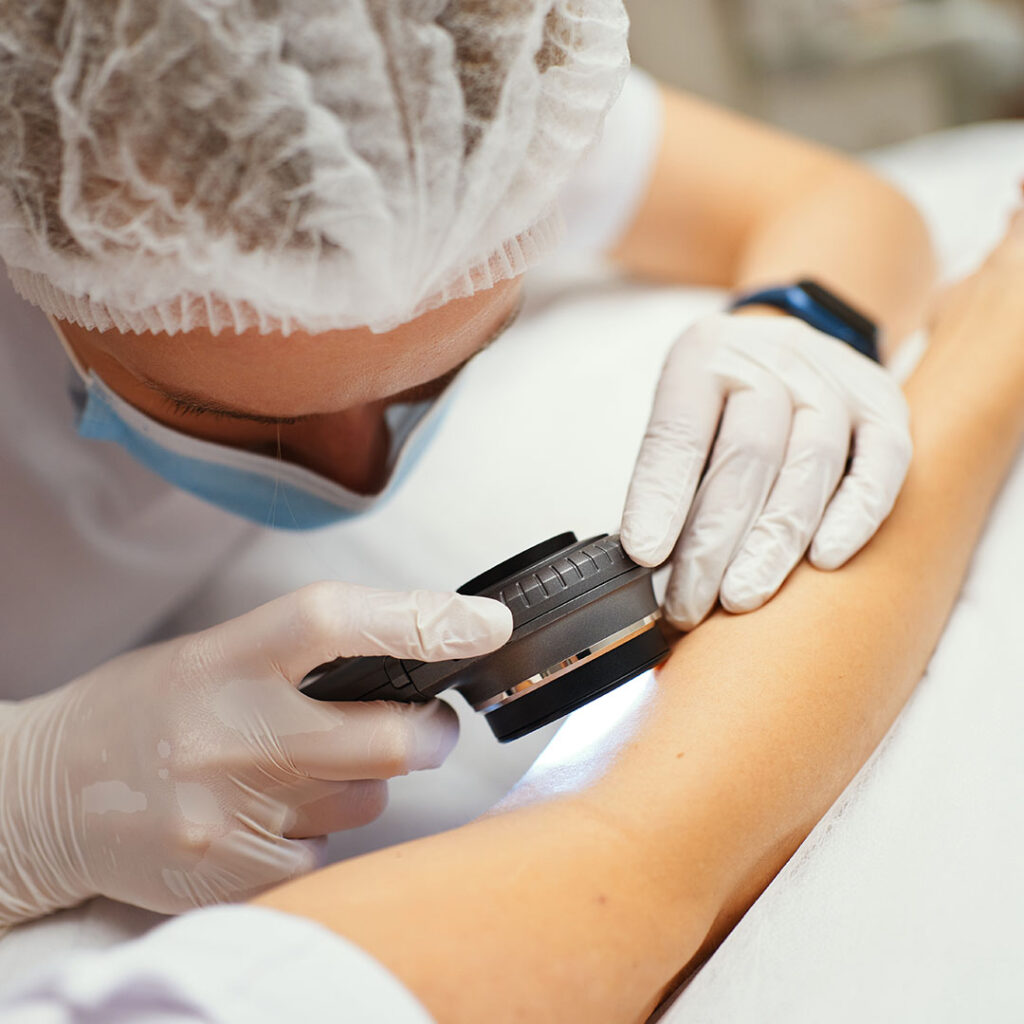
Precancerous skin conditions, also known as precancerous lesions, are changes in the skin that may develop into skin cancer if left untreated. Examples of precancerous skin conditions include actinic keratosis and dysplastic nevi.
Actinic keratosis is a scaly or crusty growth that develops on sun-exposed areas of the skin, such as the face, ears, neck, and hands. It is caused by long-term exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or artificial sources such as tanning beds.
Dysplastic nevi are moles that are larger than normal, have irregular borders, and multiple colors. They have a higher risk of turning into melanoma, a type of skin cancer that can be life-threatening if left untreated.
Early Detection and Treatment for Cancer
Early detection and treatment are critical for improving the chances of successful outcomes for cancer patients. The specific methods for early detection and treatment of cancer depend on the type of cancer and the individual patient.
For some types of cancer, such as breast, cervical, and colorectal cancer, regular screening tests can detect precancerous changes or cancer in its early stages, when it is more treatable. These tests may include mammography, pap smears, and colonoscopies.
If cancer is detected, treatment options may include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, or a combination of these methods. The choice of treatment will depend on the type and stage of the cancer, as well as the patient’s overall health and personal preferences.
In addition to medical treatment, many cancer patients also benefit from supportive care, such as pain management, nutrition support, and emotional counseling.
Early detection and prompt treatment can greatly improve the chances of successful outcomes for cancer patients, so it’s important to seek medical attention if you have any concerns or symptoms.



